Within this section you will find
A typical solar power plant will consist of
- Solar Panels
- Inverters
- Monitoring Systems
- Mounting Structure
- Balance of System
Solar Panels (Modules)
Solar panels produce electricity from sunlight (and not sun’s heat). The power generated is in the form of DC. The same panels can be used for both rooftop and ground mounted plants. A solar panel consists of
- Solar Cells
- Crystalline Silicon
- Polycrystalline
- Multicrystalline
- Thin-Film
- a-Si
- CdTe
- CIGS
- Backsheet
- Aluminium Frames
- Encapsulant EVA
- Solar Glass
- Crystalline Silicon
Inverters
Inverters convert the DC power generated by the solar plant into AC power that is either pumped into the grid or fed to onsite appliances and equipment. The inverters are the brains of a solar plant and can be very sophisticated depending on the model, incorporating charge controllers to regulate battery charging, and synchronising with gird, diesel, and other power sources.
The different types of inverters are
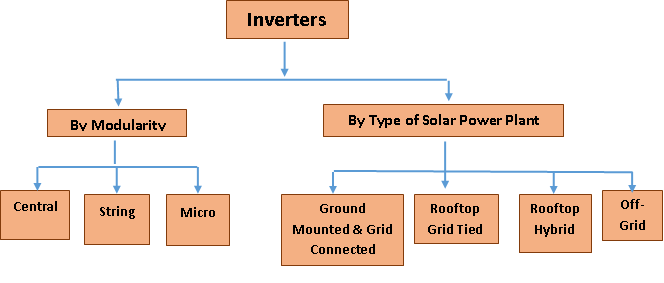
- By Modularity
- Central Inverters – A very large capacity inverter that manages power from a large number of solar panels. Its wattage is up to 100kWp.
- String Inverters – Manages power only from a string of solar panels. Multiple string inverters need to be used in large plants, which increase the cost. As these inverters are mounted much closer to the panels than a central inverter there is less loss of power from cabling. Its wattage is above 100kWp.
- Micro-inverters – Each individual panel is mounted with its own inverter. This is the most expensive option and therefore not very popular currently, but it also provides the most power generation. Its wattage will be around the module wattage range.
- Ground Mounted & Grid Connected– These inverters sync only with grid power; if grid power is not present these inverters will shut down the plant. This limits their use in rooftop plants in India as frequent load-shedding makes such an inverter an impractical choice. Grid-tied inverters are the only inverters to be used in large, MW scale solar plants. They are also used in rooftop plants.
Off-grid – These inverters are designed to work only with diesel power or battery power, but not with grid power. They are suitable only in off-grid or grid-scarce locations. Please refer to the Off-grid Section of this report for more details
Hybrid – These inverters are the most complex, syncing with grid, diesel, and battery power. They are often used in rooftop plants in India
Monitoring Systems
Often incorporated into the inverter, these systems allow the plant developer or service technicians to monitor the performance of the plant and perform preventive maintenance.
Mounting Structures
The solar panels need to be mounted at an optimal direction to the sun to maximise generation. Mounting structures are specialised structures that can hold the panels securely even during cyclones. There are different designs for ground mounted and rooftop plants.
Balance of System
These include all the other components required for a functioning solar plant. Typically
- AC Cables
- AC Distribution Boards
- AC Isolator
- Array Junction Boxes(AJB)
- Batteries (optional, usually found only in rooftop plants)
- Connectors
- DC Cables
- DC Distribution Boards
- Disconnects/switches
- Earthing Kit
- Fuses
- Lightning Protection
- Meters
- Surge Protection Devices
- Trackers (optional, usually found only in ground mounted plants)
- Single-axis
- Dual-axis
- Transformers
Related Articles
1. Solar Business Opportunities – An Overview
2. List of High Potential Sectors and Opportunities in the Solar Sector
3. Manufacturing Opportunities in Solar Energy Sector
4. Business Opportunities in Solar Thermal – Heating Applications
5. Business Opportunities in Solar Thermal – Power Applications
6. Business Opportunities in Diverse Off-grid Applications
7. Innovations and Niche Opportunities in Solar Power Sector
8. Ways to Identify Other Potential and Attractive Off-grid Segments
9. Attractive Segments and Innovations in Rooftop Solar Sector
10. Business Models for MW Scale Solar PV in India
11. Emerging Opportunities in Solar Thermal – Refrigeration & Air-Conditioning
12. Key Customer Segments for MW Scale Power Plants


