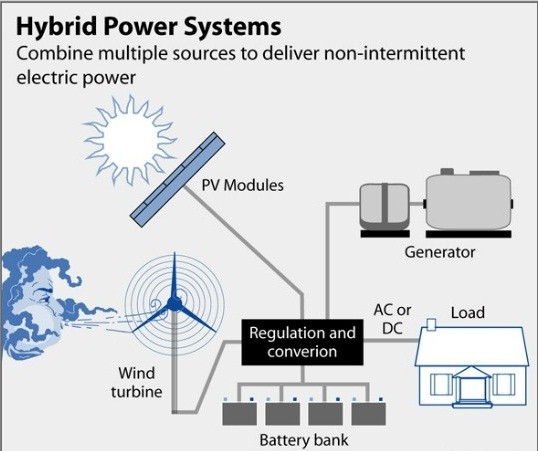
What is solar-wind hybrid power plant?
As the wind does not blow all the time nor does the sun shine all the time, solar and wind power alone are poor power sources. Hybridizing solar and wind power (min wind speed 4-6m/s) sources together with storage batteries to cover the periods of time without sun or wind provides a realistic form of power generation. The system creates a stand-alone energy source that is both dependable and consistent which is called the solar-wind hybrid system.
Generally, these solar wind hybrid systems are capable of small capabilities. The typical power generation capacities of solar wind hybrid systems are in the range from 1 kW to 10 kW.
Major components of solar-wind hybrid power plant
- Solar PV modules
- Wind turbine
- Regulation and conversion units – Inverters and electronic controllers
- Battery Bank
- Generator (if required)
How it works?
- The hybrid solar wind turbine generator uses solar panels that collect light and convert it to energy along with wind turbines that collect energy from the wind.
- Solar wind composite power inverter has inputs for both sources, instead of having to use two inverters and it contains the required AC to DC transformer to supply charge to batteries from AC generators.
- Hence the power from the solar panels and wind turbine is filtered and stored in the battery bank.
- For the times when neither the wind nor the solar system are producing, most hybrid systems provide power through batteries and/or an engine generator powered by conventional fuels, such as diesel. If the batteries run low, the engine generator can provide power and recharge the batteries.
- Adding an engine generator makes the system more complex, but modern electronic controllers can operate these systems automatically. An engine generator can also reduce the size of the other components needed for the system.
- Keep in mind that the storage capacity must be large enough to supply electrical needs during non-charging periods. Battery banks are typically sized to supply the electric load for one to three days.
Source: www.energy.gov
| Pros | Cons |
| Generates approximately twice as much as solar or wind only systems | Higher initial investment |
| Enhanced reliability of the power generation system | Not feasible in some urban locations where the wind speeds are much lesser |
| Do not require grid expansion as they produce power at different intervals and during complementary seasons | Small amounts of losses due to the shading of wind towers |
| Size of the battery can be minimized as there is less reliance on one method of power production | Cost-competitive option only in regions where wind & solar patterns complement each other |
| VAWT can be used in places where the wind speeds are low to drive an HAWT | Market maturity not yet achieved |
| Not all types of wind turbines can be utilized as the wind speed varies with regions |
To know more about the benefits & challenges associated with solar-wind hybrids, Click Here
Conclusion
The independent systems cannot provide a continuous source of energy, as they are seasonal depending on the region. One can utilize a hybrid system of wind and solar to capture the strengths of each system, while at the same time overcoming the weaknesses of each system, to create a balanced approach to producing energy. The unit cost of power can be minimized but the same cannot be guaranteed for all regions due to the variation of the solar/wind energy received.
Related Articles
- How Effective is a Solar-wind Hybrid System for Rooftops?
- What Kinds of Business Opportunities Exist in the Solar-diesel Hybrid Sector?
- How Much Roof Area Do I Require to Install a Rooftop Solar PV System?
- How Much Electricity does a Rooftop Solar PV System Generate?
- What are the Various Components of a Rooftop Solar System?